Diabetes (Mellitus) Early: Signs and Symptoms
Some signs let you know if you have diabetes mellitus and give you a chance to start treatment early before things get too detrimental. These signs depend on what kind of diabetes mellitus you might have. Diabetes means “excessive urination” and mellitus means “honey”, these two words together mean “sweetness in urine” or in other words “sugar/glucose appearing in urine”. Many forms of diabetes mellitus are due to different causes.
Diabetes may be primarily—caused by another disease, or secondary—caused by damage of the pancreas by another disease. Approximately 98% of diabetes patients have primary diabetes mellitus, the idea behind this article is to help learn about the two kinds of primary diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
Insight and self-consciousness, make it mainstream to ponder the wholeness of our health. There is an abundance of social media influencers advertising “eating plans” and “exercise regimens”. Lifestyle apps that keep you healthy by reminding you to drink water, recommending what best to eat and at what time, and ensuring you have enough breaks during the day.
Considering all these general mindfulness being the “in thing” in our society, it is alarming to see that so many people don’t understand the inner workings of their own bodies. So many people go through everyday life, experiencing the symptoms of diabetes but take it as a normal occurrence because a large number of the symptoms do not present as dangerous on their own, and that in itself is its danger. Understanding and recognising some early symptoms of diabetes can help us understand when we need to seek some form of medical consultation.
Early Symptoms Of Diabetes
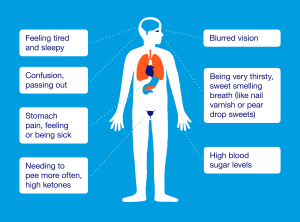 The most common signs of diabetes mellitus (both type 1 and type 2) are frequent thirst, excessive urination and increased hunger. The excess glucose (sugar) in your blood that isn’t absorbed into your body due to diabetes is diluted by water and gotten rid of by the kidneys. This is the reason for frequent urination.
The most common signs of diabetes mellitus (both type 1 and type 2) are frequent thirst, excessive urination and increased hunger. The excess glucose (sugar) in your blood that isn’t absorbed into your body due to diabetes is diluted by water and gotten rid of by the kidneys. This is the reason for frequent urination.
Because a lot of water is accompanying the glucose on the way out, the body gets dehydrated. You become thirsty and drink a lot of water to replace what was lost. Glucose and other nutrients and food groups are necessary for daily life from your everyday meals. Because there is now less glucose in your body (it has been flushed out), you start to feel hungry and crave food to compensate for the lack.
This leads to a cycle of always eating and drinking without actually getting any of the benefits. Controlling your blood glucose levels and keeping them optimal makes it possible to live life normally, eating and drinking whenever you wish without a condition forcing you to.
It is sad to see that these symptoms are so often written off as ‘normal’, but it is understandable. A busy person will not think thirst or a little nausea is a big deal, and even the more severe symptoms closely resemble the symptoms of a common cold or flu that goes away on its own after some days of rest and many bowls of chicken soup.
Not enough people realise that all these signs hint at the body’s inability to absorb glucose, which is caused by a lack of or insulin resistance—the hormone that transports glucose to where it’s needed. To be on the safe side, if after being sick your thirst still lingers, a visit to the doctor should be the next thing on the list. One single blood test can clear years’ worth of doubt.
The human body extracts glucose from food to use it as fuel. Every process in the body requires it, like how a car needs gas to run. The cells, tissues, and organs get the glucose that’s digested in the stomach after it has been transported out by insulin. Therefore, without insulin, there would be no energy for you to do work. The body would stop functioning properly.
The unique combo of continuous thirst, frequent urination, and sudden weight loss are key signs of an increased amount of glucose in the blood. These three symptoms are common in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are different branches of the same disease. They are both caused by problems regarding insulin. This difference between the two types is the reason why the rest of the symptoms begin to vary after the early stages.
In Type 1 diabetes, the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to transport all the glucose you eat to where it is needed, so the rest remains in the blood.
In Type 2 diabetes, the pancreas produces enough insulin but the body does not recognise it so it cannot use it, and that causes the glucose to remain in the blood.
Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes happens suddenly and at any age in life—but usually it occurs before the age of 40. It happens when the pancreas stops secreting insulin. It is caused by degeneration of the cells of the pancreas, damage to the pancreas due to autoimmune diseases, a congenital disorder of pancreas cells or destruction of those cells by viral infection.
When it occurs in infancy or childhood, it is called ‘juvenile diabetes’. It can take weeks or months for the pancreas to completely stop secreting insulin, but eventually, a normal, healthy person will become insulin-deprived and their glucose levels will shoot up to dangerous levels. A patient with Type 1 diabetes will become dependent on insulin injections for treatment so Type 1 diabetes is also called Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM).
Since the body can’t access the glucose in the blood, it begins to find alternate sources of energy and starts breaking down fat and muscle. The end products of this are ketones (ketoacids).
The abundance of these acids makes the blood more acidic and leads to acidosis. This will cause fatigue, lack of appetite, and confusion.
When the ketone level in your blood is very high, your heart will begin to beat faster, and your breathing rate will increase. Your breath will have a sweet, fruity smell because of the many ketones present in the bloodstream—and at this stage, the amount would have reached a life-threatening level that can cause unconsciousness.
Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is caused by a partial deficiency of insulin caused by the body’s cells not being able to receive the hormone even after it has been produced. It is the more common type of diabetes and usually occurs after the age of 40. Only a few forms of it required insulin as treatment. It can be controlled by taking oral hypoglycemics (drugs that make the body more receptive to insulin/increase insulin production). Because of this, this type of diabetes is also called noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM).
Insulin Resistance can be caused by genetic factors, stress, or lifestyle changes. Examples of these lifestyle changes are bad eating habits and lack of physical activity which leads to obesity. Physical activity helps a person burn glucose and makes their body more sensitive to insulin while being overweight increases insulin resistance (scientists aren’t completely sure why).
A patient with Type 2 diabetes does not need insulin in the beginning because the pancreas overproduces to compensate for the unreceptive cells—this is the reason why Type 2 diabetes often goes unnoticed for years. But eventually, the pancreas isn’t able to keep up and the glucose builds up in the blood even with insulin being constantly produced. Eating healthy, cutting back on sweets and losing excess weight helps control the glucose levels in a person with type 2 diabetes. Early treatment positively impacts and maintains a good quality of life.
Spotting Diabetes (Mellitus) Early: Signs and Symptoms
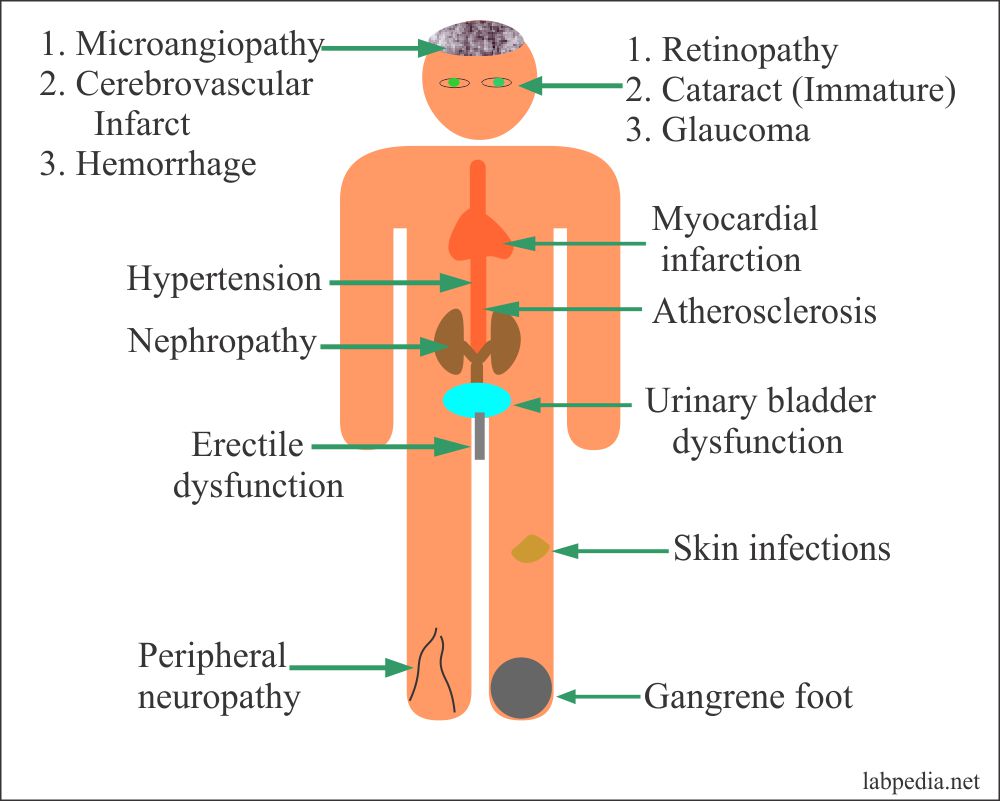
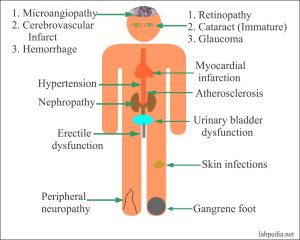
Complications Of Diabetes Mellitus

Prolonged hyperglycemia (high blood glucose levels) damages the retinas of your eyes (which spoils your vision). When caught early, this condition is manageable, but if left untreated, Diabetic Retinopathy will cause permanent damage to the retina of the eyes. Not only this, high glucose levels can damage the kidneys (Diabetic Nephropathy) and nerves (Diabetic Neuropathy) of the body as well as hypertension and heart attack.
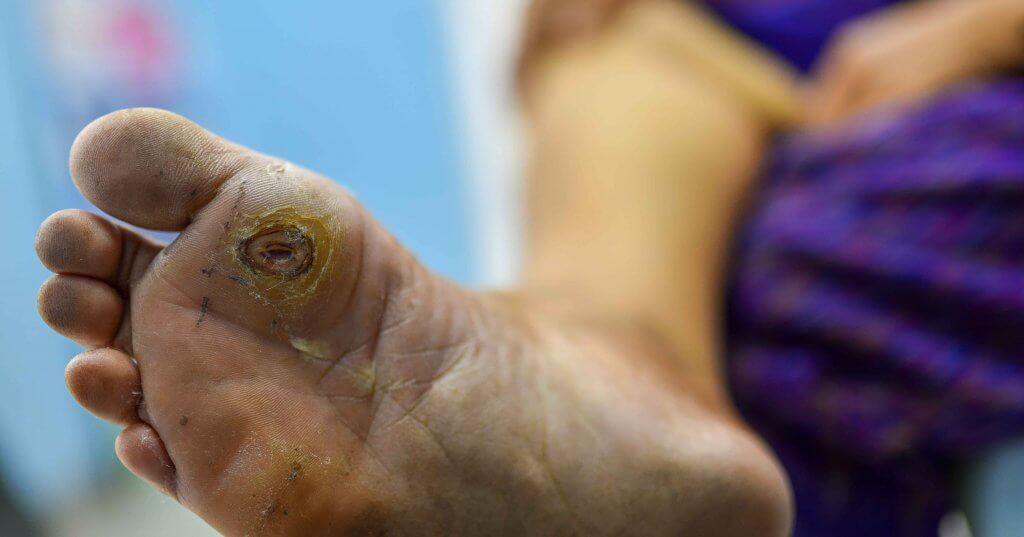
A person with diabetes is more prone to getting fungal infections, and when they are infected it is quite hard to treat. Yeast grows from sugar and is naturally occurring in the body but when too much yeast accumulates it causes pain and itching. It grows in moist and warm places like the mouth, the folds of the skin, the genitals, the eyes, and the foot (especially the toenails).
Without treatment, such infections can lead to blindness or become life-threatening when the yeast manages to get into the bloodstream of a patient who has a depressed immune system and spreads to other parts of the body.
The high blood glucose also causes slow wound healing due to lack of energy and the neuropathy of the nerves will prevent you from feeling pain sensations, so a lot of tiny wounds become ulcers and if left untreated can cause problems later on.
For this reason, it is always good to pay close attention to the state of your body and catch these signs and symptoms before they progress too far and become deadly. Early intervention and correction of elevated blood glucose can promote proper circulation and healing while preventing the onset of all these complications.
Juvenile Diabetes:
Young children aren’t able to properly convey the changes that occur in their bodies due to a lack of understanding or communication skills. Because of this, it’s hard for parents to tell whether their children are suffering from Type 1 diabetes, especially since the symptoms are so easy to miss—being very hungry and very thirsty are easily noticeable signs but these are also just normal behaviours of growing children and shouldn’t be a cause for alarm.
The following are some behaviours observed in children with Type 1 diabetes:
- Getting yeast infections (thrush).
- Acting out of character. Being moody or restless. Having mood swings.
- Losing weight despite having frequent meals.
- Feeling tired, dull, and lacking the strength to play.
- Peeing more, or even wetting themselves despite having been toilet trained.
- Having a sweet-smelling breath
If while watching their children grow, parents notice any of these symptoms of elevated blood glucose levels in their infants, toddlers, or young children they should immediately seek their pediatrician’s guidance.
Type 1 diabetes can strike at any age. The sudden pause in Insulin production leads to a rapid rise in glucose levels which can quickly become Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA). Catching these signs early can ensure that insulin is given promptly and the quality of life is preserved.
When to See a Doctor
The symptoms of diabetes in the early stages can easily be confused as a minor illness, so it can be hard to pinpoint exactly whether you or someone you care about, has it. But that’s okay.
If you want to confirm whether what you have been experiencing could have been diabetes, you can ask yourself these questions:
- After getting a cold or the flu. Do you recover quickly? Do you still feel sick?
- Have you noticed any cuts and grazes that seem to be taking longer than usual to heal?
- Do you experience numbness and tingling in your hands or feet? Is this a recent development or a long-term condition?
- Have you always wrestled with yeast infections, or are recurring infections a new struggle?
- Have you noticed weight loss you can’t explain? Are you overweight?
- Have you felt thirstier, or found yourself drinking more than usual in recent weeks or months?
- Have you noticed any changes in your vision?
Catching It Early Makes All The Difference
If you are concerned about your health, visit your physician and tell them your concerns. A simple test strip or lab draw can supply you both with a wealth of information about if necessary, treatment can be started. Early diagnosis and treatment by a professional make all the difference between managing your condition and having to suffer unknowingly.
Since 2012, our goal at mySugr has always been to make diabetes suck less for people within the diabetes community. We have long endeavored to educate, advocate, and elevate the global working knowledge of living life with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes to the fullest. Utilizing our combination approach of sound coaching and advancing tech, we’ve made huge strides at creating an environment that lets all people with diabetes maintain optimum health while living their best lives!
Diabetic And Unaware
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the number of people with diabetes rose from 108 million in 1980 to 422 million in 2014—”About 422 million people worldwide have diabetes, the majority living in low-and middle-income countries, and 1.6 million deaths are directly attributed to diabetes each year.”
According to the American Diabetes Association, in 2018, 10.5% (34.2 million American adults) of the American population had diabetes. 24.8 million were diagnosed and 7.3 million were undiagnosed. And 1.5 million Americans are diagnosed with diabetes every year.
This means that right now millions of people walking around with a dangerously high amount of glucose in your blood, experiencing complications, and receiving no treatment for them. We hope that everyone reading this gains an understanding of diabetes, whether they have it or not.
We know that it is improbable to reach everyone, but if you can help spread awareness and educate those around you on the symptoms of early-stage diabetes, that means an increased awareness in your community, which can reduce the number of undiagnosed diabetic patients in your direct environment.
If you have a family member or relative who has been diagnosed as being diabetic, to be on the safer side, you should visit your doctor to discuss the possibility of being at risk. A bi-annual blood test can provide a constant baseline for your doctor to monitor for any unusual increase in blood sugar levels.

If you or your child struggle to maintain a healthy weight, ask your doctor and/or your child’s pediatrician for pre-screening and lab work to look out for early signs of diabetes. By working hand in hand to achieve optimum health, you and your medical team can be proactive partners in warding off any symptoms of diabetes before they begin to damage peripheral systems.
If you or your child have other genetic factors (such as other auto-immune conditions), you should ask your doctor for pre-screening lab work to rule out any signs of diabetes. Auto-immune conditions tend to breed additional auto-immune conditions. Still, by creating a teamwork approach to full-body care, you can provide a protective screening system that stands sentry against the early warning signs of diabetes. In this way, you can begin any treatment at the earliest possible opportunity and set the stage for successful long-term health.